
Introduction
Telecom companies have evolved at an exponential rate. Beginning from Traditional interface (FXO/FXS) to Digital interface (T1/E1 PRI) and the latest VOIP (3G/4G/VoLTE). With humble beginnings in the ‘90s, according to Statista and Tech.co, VoIP usage especially as Business phone systems has seen an abrupt rise in just a gap of 8 years i.e. between 2010 & 2018 in the USA.
What is interesting from these statistics is that small and mid-size businesses saw a large surge in adoption of VoIP even while remaining lower to residential adoption of VoIP services.
The scenario in India
According to Financial Express, the government data shows, as of March 27, 2022, there were 79.27 lakh MSMEs in India. These MSMEs are expected to outperform in the coming years due to their inherent potential in the three-sector model of the country. These aspiring MSMEs, at least the majority of them might still be using legacy telephony connected to traditional interfaces, that include analog systems like PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network), POTS (Plain Old Telephone Service Lines), etc.
Traditional systems have their own challenges that can hinder the growth and expansion of these aspiring MSMEs. Simultaneously, there also lie challenges in upgrading to modern systems while keeping the legacy systems intact. Therein comes the role of Business IP Phone systems, which can integrate well with legacy systems thus protecting your investment that was made earlier.
What are Business IP phone systems?
An IP (Internet Protocol) phone is a device that uses the internet as a medium to exchange information by converting it into packets that are then transmitted over the internet.
Along with it comes various systems that aid IP phones to integrate as well as function with Legacy systems like PSTN. The systems include VOIP Gateways, IP-PBXs (Private Branch Exchange), SIP telephones, etc.
Traditional phones use PSTN, dedicated infrastructure as opposed to the IP which requires just an Internet or LAN (Local Area Network) as a medium to communicate.
The 7 benefits of IP phone systems
Unified Communication
Unified communication means that it integrates multiple enterprise communication tools such as voice calling, video conferencing, instant messaging, presence sharing, etc. Traditional telephony limits you to just Voice calls, but with IP telephony you can exchange information over the web, video, and audio through the data network. This can aid and ease the communication between Employees and Employers.
Mobility
Employees can access and exchange information from anywhere and anytime, especially by integration with softphones. An employee with the internet can make and receive calls while on the move.
Scalability
Scaling your communication becomes much easier with IP phone systems thus ensuring your investment is future-proof. For instance, VOIP uses up less space due to its wireless nature. Hence, with the limited infrastructure, you can get more benefits out of it as compared to traditional telephony.
Cost-effective
The data costs especially considering Telecom companies in India are much more competitive, thus our dependence on VOIP services has become cost-effective in recent years. VOIP telephony also, sustains on minimum infrastructure compared to traditional telephony, thus reducing maintenance costs.
Productivity
IP telephony supports a wide range of features like Teleconferencing, Voicemail to Email transcription, IVR (Interactive Voice Response), etc. aiding employees to work more efficiently. This efficiency can reflect in the productivity of the employees and the organization as a whole.
Feature-rich
IP phones have the potential to do more than mere calling. Features like teleconferencing, auto-attendant, voice-mail to e-mail transcription, call-waiting, etc are some of them that give IP an edge over traditional telephony.
Quality
The quality of information traveling through VOIP is much higher than the traditional ones as there are minimal losses during transmission. The key to VOIP call quality is robust connection and bandwidth.
But they do have challenges!
Power
Since VOIP runs on power drawn from the wall socket, it constantly requires power to operate. In case of a power outage, a provision for emergency source power also needs to be arranged to prevent barriers to communication.
Internet Service Provider’s (ISP) End
The communication depends on the quality of service from the ISP’s end. In case of any disruption, the entire communication channel can face an impact.
However, this does not demean the potential of IP Phone systems in India.
Matrix Comsec is a living example. As a Top Telecom company in India for more than 3 decades, it has not only served the sector, but also the nation. To know more about our Telecom products and solutions, connect with us.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What is the difference between IP Telephony and PSTN?
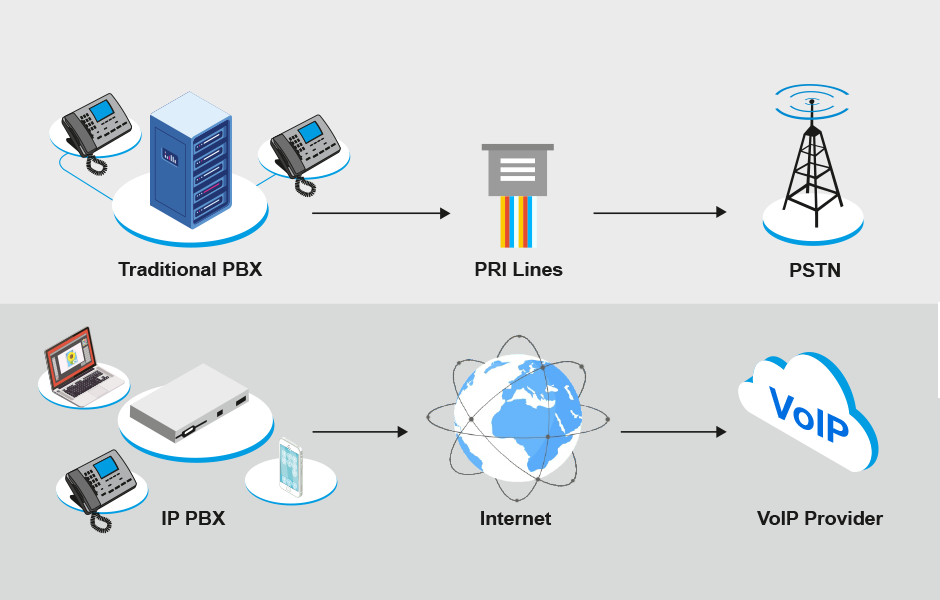
PSTN (Public Switched Telephone Network) deals with dedicated circuit switching for transmitting information while IP telephony deals with transmitting information in packets.
PSTN involves a direct connection between two communicating parties hence no other can communicate through it. In IP as packets are involved, hence multiple packets of information from different parties can be communicated through a single line.
Can IP phone systems be connected with PSTN?
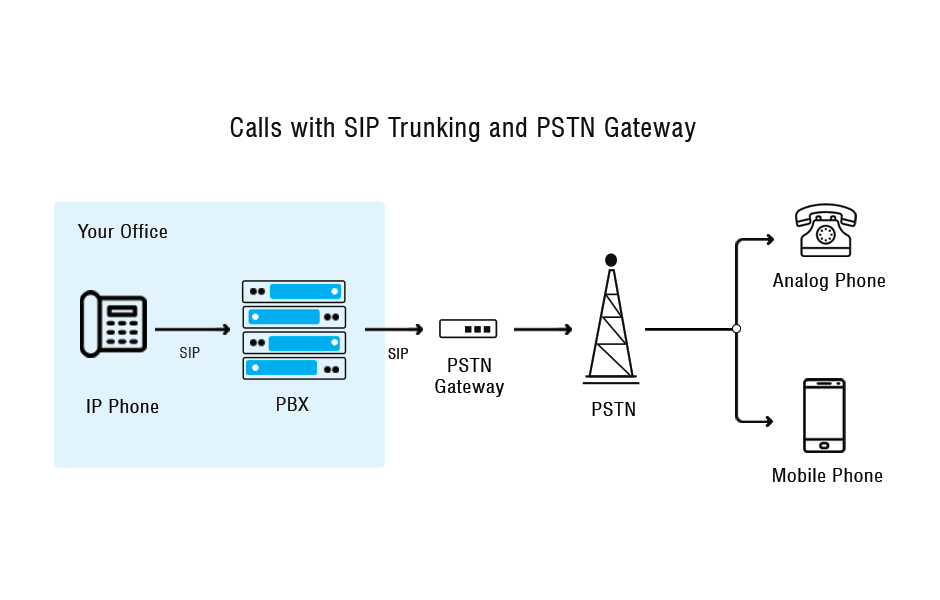
IP Phone systems can be integrated with traditional networks with the help of Media Gateways. These devices convert the information packets from IP Telephony into TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) voice to be sent over the traditional PSTN.
What is the difference between SIP (Session Initiated protocol) and PRI (Primary Rate Interface) Trunks?
SIP and PRI are two different communication technologies, which connect your business to a PSTN. SIP uses the internet as a medium to send information whereas PRI uses a dedicated physical connection to send information
What is the difference between T1 and E1 PRI?
T1 and E1 PRI are two access methods of ISDN (Integrated Services Digital Network). The two methods differ in the number of channels they carry and the region they are in use.
An E1 is 30 ‘B’ channels, two ‘D’ channels, and one timing and alarm channel, E1 channel is used in most parts of the world.
In North America, PRI service is delivered on one or more T1 carriers (often referred to as 23B+D).
